把程序部署到Tomcat或WebLogic后,经常碰到结束程序时不能完全结束,某些线程还活着,必须手动强制关闭整个服务器才可以结束.但如果我们的应用服务器上部署了很多个重要应用,其中一个应用的启停应该不能影响其他应用才对.究竟是什么原因导致了我们的服务器不能关闭呢?估计很多人没有深入研究过这个问题吧.
先看看下面的例子吧:
package com.tgb.lk.thread;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadDemo {
private Timer timer;
private ExecutorService threadPool;
private Thread thread1;
private Thread thread2;
private Thread thread3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadDemo threadDemo = new ThreadDemo();
threadDemo.init();
try {
Thread.currentThread().join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
public void init() {
// 1.启动Timer
timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}, 0, 3000);
// 2.启动线程池
threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int inner = i;
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(inner);
}
});
}
// 3.线程挂起
thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000000);// 如果时间设置的超长,看上去也相当于挂起了线程.
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
});
thread1.start();
// 4.线程挂起2
thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.currentThread().join();
Thread.currentThread().wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
});
thread2.start();
// 5.线程挂起3
thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread().suspend();// 挂起当前线程,可能会形成死锁哦,所以不建议使用suspend
}
});
thread3.start();
}
}
执行后我们会发现main方法不能自动结束,原因当然是init方法中的一些线程阻塞了程序结束.如何验证我的想法呢?
使用JConsole可以查看,如果你还没听过这个工具就有点out了,JDK5+都自带这个工具.

当我们注释掉代码中main方法的Thread.currentThread().join();后再运行看Jconsole线程,结果如下:
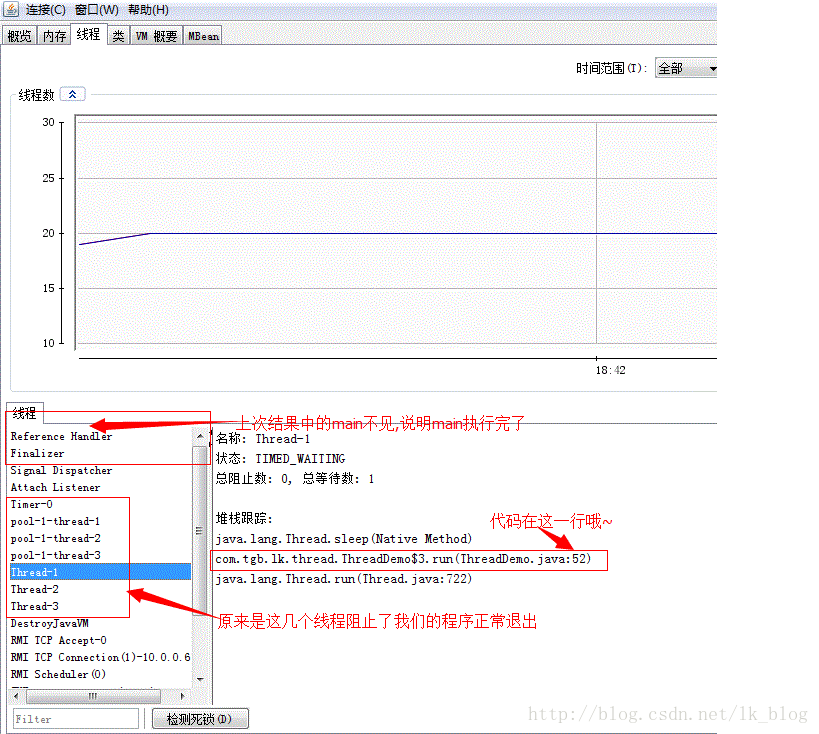
原来Timer, 线程池, 线程操作中的sleep,wait,suspend等方法都能阻止我们的线程结束啊,找到原因了就找解决办法吧,看下面代码:
package com.tgb.lk.thread;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadDemo {
private Timer timer;
private ExecutorService threadPool;
private Thread thread1;
private Thread thread2;
private Thread thread3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadDemo threadDemo = new ThreadDemo();
threadDemo.init();
// try {
// Thread.currentThread().join();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// }
threadDemo.destory();
}
public void init() {
// 1.启动Timer
timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}, 0, 3000);
// 2.启动线程池
threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int inner = i;
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(inner);
}
});
}
// 3.线程挂起
thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000000);// 如果时间设置的超长,看上去也相当于挂起了线程.
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
});
thread1.start();
// 4.线程挂起2
thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.currentThread().join();
Thread.currentThread().wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
});
thread2.start();
// 5.线程挂起3
thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread().suspend();// 挂起当前线程,可能会形成死锁哦,所以不建议使用suspend
}
});
thread3.start();
}
public void destory() {
if (timer != null) {
timer.cancel();
}
if (threadPool != null) {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
if (thread1 != null) {
thread1.interrupt();
}
if (thread2 != null) {
thread2.interrupt();
}
if (thread3 != null) {
thread3.stop();
}
}
}
这段代码相比第一段代码我们在main中调用了
destory这个
方法.destory方法结束了timer,threadPool等对象的线程.运行一下代码,结果程序可以自动结束了,这时已经不再需要jconsole了.
拓展一下, 很多程序都用spring来管理,如果在spring创建了线程,这些线程希望在spring结束时才去结束该怎么办呢?
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class ClazzDaoImpl implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//这里写初始化的方法
// init()
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
//这里写结束线程的方法
// destory()
}
}希望读者能从上面的过程中学到调试这种问题的思路和方法,同时写代码时多多注意线程问题,自己的程序开启了对象尽量在自己的程序中同时写上结束对象的方法.
来个总结,很多程序员会用Timer,会用线程和线程池,可是很少人关心这些对象的回收,如果这些线程不回收就会造成应用服务器结束不掉,有时还会造成内存溢出.有些人可能说我很会写框架,但为什么流行度不广呢,因为咱们通常都考虑的太少,看看国外的优秀框架.是不是很多类里面都有init和destory方法,这些框架大多数都考虑了对象的回收问题.作优秀的程序员,从优秀的代码习惯开始吧~
